Understanding what is disaster recovery plan
A disaster recovery plan describes instructions that standardize how a specific organization responds to Interruptive events that include cyber-attacks, natural disasters, and power cuts. An Interruptive event may also result in brand authority loss and customer trust loss.
A disaster recovery plan is a detailed document that Summarizes how to minimize the effect of disasters and how to immediately get the organization on track. To make it effective, Arrange the plan by their location and type of disaster which can give clear, step-by-step guidelines for everybody to follow easily.
Guidelines for preparing and implementing a DRP
Leading the recovery of essential IT systems with data and business operations after disasters is what a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) accomplishes. The plan enables businesses to reduce operational interruptions and restore missing data while sustaining their operational continuity. The production of an effective DRP follows these complete steps for implementation.
Analyze Business Needs
A disaster recovery plan starts by determining critical business functions that need to be operational even during a crisis such as servicing customers and handling business finances. This aids in resource allocation and guarantees that critical systems are addressed first during recovery.
Conduct A Risk Analysis
Well-known tech giants understand the implications of cyber-attacks, natural calamities, and system crashes. Identifying risks assists businesses in mitigating threats, avoiding delays, troubleshooting, and staying protected.
Outline Recovery Aims
Setting precise recovery targets guarantees reasonable downtime. The systems loophole recovery time that must be restored and the point of data that can be ignored or lost are the recovery time objectives and the recovery point objectives respectively. These help determine the answer to the recovery question.
Pick a Recovery Method
Business has to decide on an optimum recovery technique, which may include routine data center compliance backups, cloud storage, or real-time replication. Recovery speed combined with minimal interference with business operations is what the strategy aims for.
Establish a Disaster Recovery Response Team
Properly assigned teams enhance the recovery pace. The team leader is responsible for managing the response operations, the IT personnel work on restoring systems, the communications personnel inform other employees and stakeholders about the necessary changes to the normal organizational procedures to ensure harmonious coordination to achieve the stated goals.
State the Strategy
A complete documented DRP contains step wise recovery procedures, contact details of relevant personnel, business recovery checklist, business recovery contingency checklist, information on networks and systems critical to recovery, an
Monitor and Improve Continuously
After a crisis or a test, Analyze how well the plan worked and Recognize what went right and what can be improved also Continue monitoring new risks and threats to stay prepared.
Steps to Implementing an Effective Disaster Recovery Plan
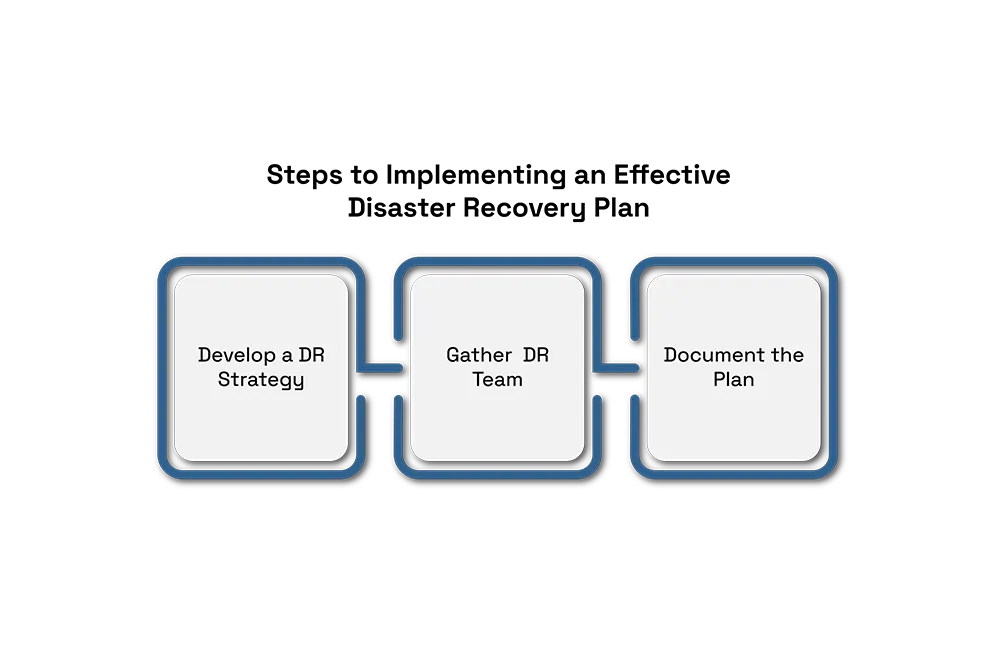
Develop a DR Strategy:
Cloud: Cloud-based DR solutions like AWS Disaster Recovery offer fast scalability and cost-effective options.
On-premises: Traditional on-site backup requires physical infrastructure but provides full control.
Hybrid: Balances the benefits of both approaches.
Gather DR Team: Assign roles like DR coordinator, IT professionals, and communication specialists and make sure each team member knows his or her responsibilities At the time of disaster.
Document the Plan: Create clear, step-by-step recovery instructions. Include infrastructure diagrams, application dependencies, and contact lists for vendors and employees.
Backup Solutions:
Regularly schedule backups to secure data and Use data replication for critical systems to minimize downtime.
Test the DR Plan: Conduct drills to simulate scenarios like power outages or server crashes. Identify gaps and refine procedures.
Monitor and Update: Technology evolves, so periodically review and adapt the DR plan to incorporate changes in infrastructure, software, or organizational priorities.
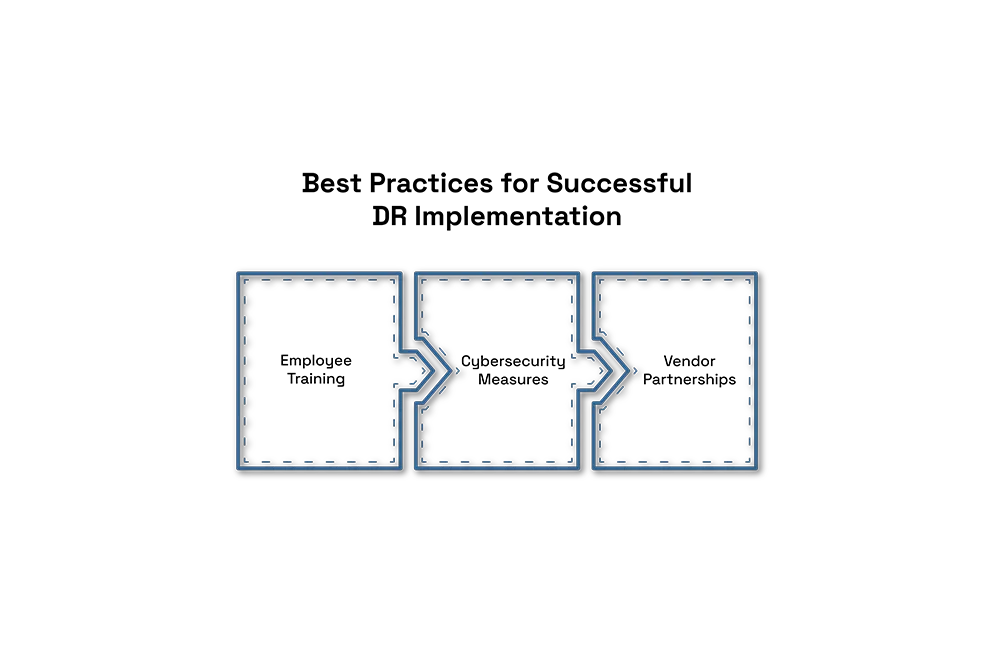
Best Practices for Successful DR Implementation
Employee Training: Equip employees with knowledge of protocols during disasters. Conduct regular workshops and refreshers.
Cybersecurity Measures: Use advanced threat detection, multi-factor authentication, and encrypted backups.
Vendor Partnerships: Work with trusted providers for backup and recovery tools. Evaluate their SLAs for uptime and data recovery.
Automation: Implement tools that automatically trigger recovery processes, reducing response times.
Compliance: Align with standards like ISO/IEC 22301 or GDPR to meet industry requirements.
Conclusion
Disaster recovery is not just an IT concern but a business necessity. By proactively planning, testing, and updating DR strategies, organizations can mitigate risks, reduce downtime, and ensure long-term resilience.