The distributed computing model which edge computing implements processes data directly at network interfaces that are close to their origin points instead of depending on centralized data facilities. The traditional infrastructure faces challenges in managing latency because IoT devices expand rapidly together with real-time applications. Modern infrastructure needs edge computing solutions because it solves essential issues facing modern operations.
Edge computing will establish itself as a vital infrastructure in 2025 because of remarkable increases in AI together with 5G (cost of 5g infrastructure) and IoT conditions. Autonomous vehicles and industrial automation alongside smart cities require real-time data processing which edge computing helps perform faster while it lowers demands on centralized cloud infrastructure. The combination of AI-based edge devices and Wi-Fi 7 alongside 6G trial networks will drive better processing power toward network locations. Businesses will implement AI-controlled edge data centers that use liquid cooling systems together with renewable power solutions to achieve optimized results while preserving environmental standards. Fast decisions will become possible as well as better security with localized data management so businesses can provide continuous digital services throughout the healthcare retail and finance industries.
The Evolution of Infrastructure
In the past, traditional systems depended on centralized data centers, which Frequently resulted in slow data processing and high bandwidth usage. With the arrival of cloud computing, we saw improvements in scalability but it also brought about delays for applications which need real-time responses. Now, edge computing is changing the game by processing data closer to where it is generated. This allows for faster and more efficient operations since data can be handled locally.
Understanding What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a process of getting data close to its source, like on system or local servers, rather than sending everything to faraway data centers which helps to make things faster and reduces the amount of data that needs to travel over the internet.
How does edge computing work?
Devices furnished with sensors generate data. In place of sending all the data to a central location it is processed locally at the edge and only sensitive information is sent to the cloud for further analysis.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Faster Response Times:
Edge computing processes the data closer to its source, that means it takes less time for data to travel from devices to central data centers. This speed is especially important for applications that need quick response.
Better Reliability:
It makes applications more reliable by reducing the need to depend on central data centers.
Easier to Scale:
Edge computing allows organizations to easily add more computing power by spreading resources across many edge devices. This setup helps businesses adjust their infrastructure to meet changing demands without putting too much pressure on central data centers.
Improved Data Privacy and Security:
By transforming sensitive information locally, edge computing helps to address privacy concerns that come with sending data to central data centers. This local processing approach improves data privacy and security
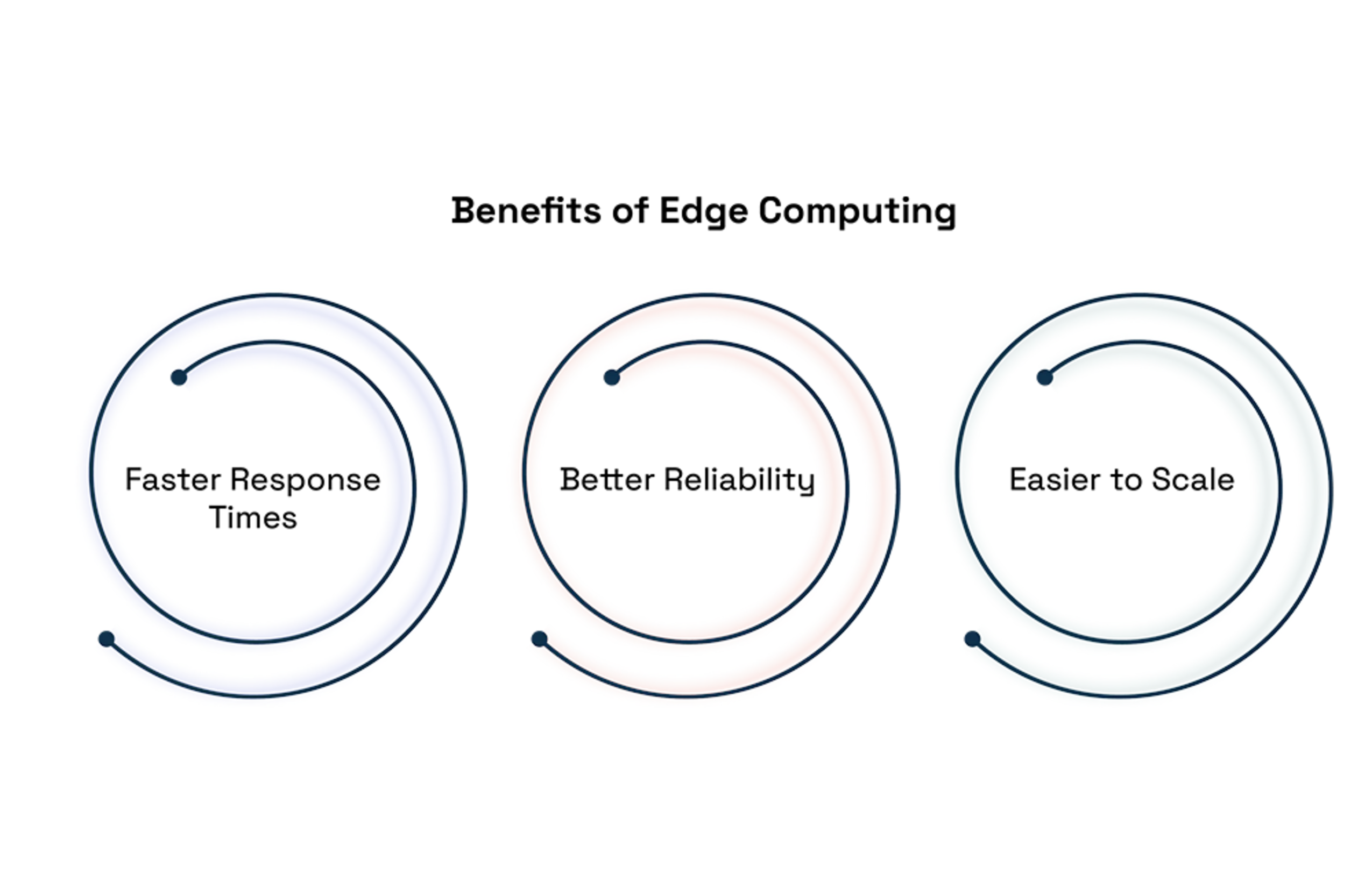
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
The impact of edge computing extends in various industries, transforming business processes, improving customer experiences.. Some applications of edge computing include:
Smart Cities: Edge computing is used to improve city services, like smart transportation systems, public safety programs, and monitoring the environment.
Retail: In stores, edge computing helps to create Customized shopping experiences and provide real-time data
Healthcare: Edge computing supports healthcare by allowing remote monitoring of patients, and analyzing patient data in real-time during critical care situations.
Applications of Edge Computing in Modern Infrastructure
IoT Devices like smart Thermal sensors and connected appliances use local data processing to respond faster to changes.
Wearable devices and telemedicine use edge computing to analyze patient data right away, improving diagnosis and treatment.
The Future of Edge Computing in Infrastructure
5G Networks:
The Deployment of 5G will Enhance edge computing’s capabilities which enables the ultra-low latency for applications like AR/VR and smart cities.
AI and Machine Learning:
Edge computing enhances applications by processing data locally and reducing the need for cloud interaction.
Conclusion
Edge computing is no longer a luxury but a necessity in modern infrastructure. It empowers organizations to meet the demands of real-time data processing, scalability, and efficiency. Businesses that adopt edge computing are poised to lead in an increasingly digital and decentralized world.
Did you know?
Edge computing marketplace is projected to surge from roughly $34 billion in 2024 to more than $700 billion in 2033.