A few critical patterns are molding the Next Chapter in cloud computing for data centers. Artificial intelligence is coordinated at each level, from managing energy efficiency and predictive maintenance to building specialized AI infrastructure for machine learning workloads. This integration drives significant spending, including Amazon Web Services (AWS) wanting to contribute $11 billion to grow a computer-based intelligence foundation in Georgia.
Edge computing is gaining importance as data centers are being positioned closer to end users, resulting in reduced latency and enhanced performance. This trend is further supported by the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, to make data centers more environmentally friendly. Additionally, innovations in liquid cooling technology are improving energy efficiency by decreasing the amount of power needed for cooling and overall operations.
These improvements highlight a future where data centers are more effective, manageable, and ready to fulfill the developing needs of man-made intelligence and cloud services.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing offers types of assistance including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence through the internet (“the cloud”). It enables faster innovation, greater flexibility, and cost-efficiency. By paying only for the services you utilize, businesses can less operating costs, optimize infrastructure, and scale according to their needs.
Why use data centers in cloud computing?
Cloud and Data centers are fundamental in distributed computing since they give the genuine establishment expected to store, manage, and process the high amounts of data required by cloud services. These facilities house servers, storage systems, and networking equipment that enable businesses to access and utilize cloud services reliably and efficiently. Data centers give versatility, high accessibility, and security, which are significant for distributed computing to fulfill the needs of organizations and clients. Also, they support efficient energy use, disaster recovery, and quick information handling, assisting associations to convey services with insignificant free time.
What is Infrastructure as a Service?
This service provides a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the digital. It gives organizations on-request admittance to principal foundation including servers, stockpiling, organizing, and other processing assets without the expectation to claim or keep up with equipment Parts. With IaaS, associations can scale their foundation as indicated by request, lessen forthright expenses, and pay just for the assets they use. This approach is Ideal for businesses requiring scalability, flexibility, furthermore, command over their frameworks and applications.
What is Software as a Service?
This service is a cloud computing model that conveys programming applications over the internet. Rather than introducing and keeping up with programming on individual gadgets or servers users can access and use the software through a web browser. This Service is typically subscription-based, with users paying for the services they use regularly. This model eliminates the need for businesses to manage or update software, as the provider handles maintenance, security, and updates. Ordinary instances of SaaS incorporate applications like Gmail, Microsoft Office 365, and Dropbox. This help is famous for its benefit, versatility, and cost-viability.
What is Platform as a Service?
This help is a cloud computing model that offers a stage empowering clients to create, run, and oversee applications without managing the intricacies of basic foundation. This helps offer a structure that incorporates working frameworks, information bases, improvement instruments, middleware, and different administrations expected for application improvement.
IIt empowers designers to zero in exclusively on coding and application rationale while the cloud supplier deals with the equipment, systems maintenance, and programming upkeep. This Service is utilized for building web applications, versatile applications, and services, and it offers adaptability, cost productivity, and the capacity to rapidly convey applications. Well-known instances of PaaS incorporate Google Application Motor, Microsoft Purplish Blue, and Heroku.
What Is The Future of Cloud Computing?
Quantum computing: It promises to revolutionize data processing, enabling faster problem-solving for complex computations and optimization operations, which could decisively further develop cloud administrations in regions, for example, cryptography, AI, and information examination.
Edge computing: With the appeal for low-idleness applications for example IoT and 5G, edge registering processes information nearer to the end client or contraptions, reducing inactivity, extending execution, and facilitating stress on concentrated data centers.
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud: Businesses are by improvement using a mix of public, private, and hybrid clouds to avoid vendor lock-in, increase redundancy, and optimize for price and performance. Multi-cloud systems get permission from organizations to manage responsibilities across multiple providers, while half-breed mists provide compatibility by joining on-premises and cloud-based resources.
Serverless Computing: Serverless figuring abstracts away framework the executives, empowering engineers to focus on composing code. With a serverless stage, designers can consequently scale their applications on request, upgrading asset utilization and lessening costs.
Artificial Intelligence: AI and ML are incorporated into cloud administrations to empower robotization, prescient examination, and improved navigation. Cloud providers are dynamically offering AI knowledge contraptions that grant associations to harness the power of huge data without an in-house system.
Internet of Things (IoT): Cloud computing plays a main role in managing the high amounts of data generated by IoT devices. The cloud gives the framework expected to store, break down, and follow up on IoT information, empowering savvy urban communities, enterprises, and services.
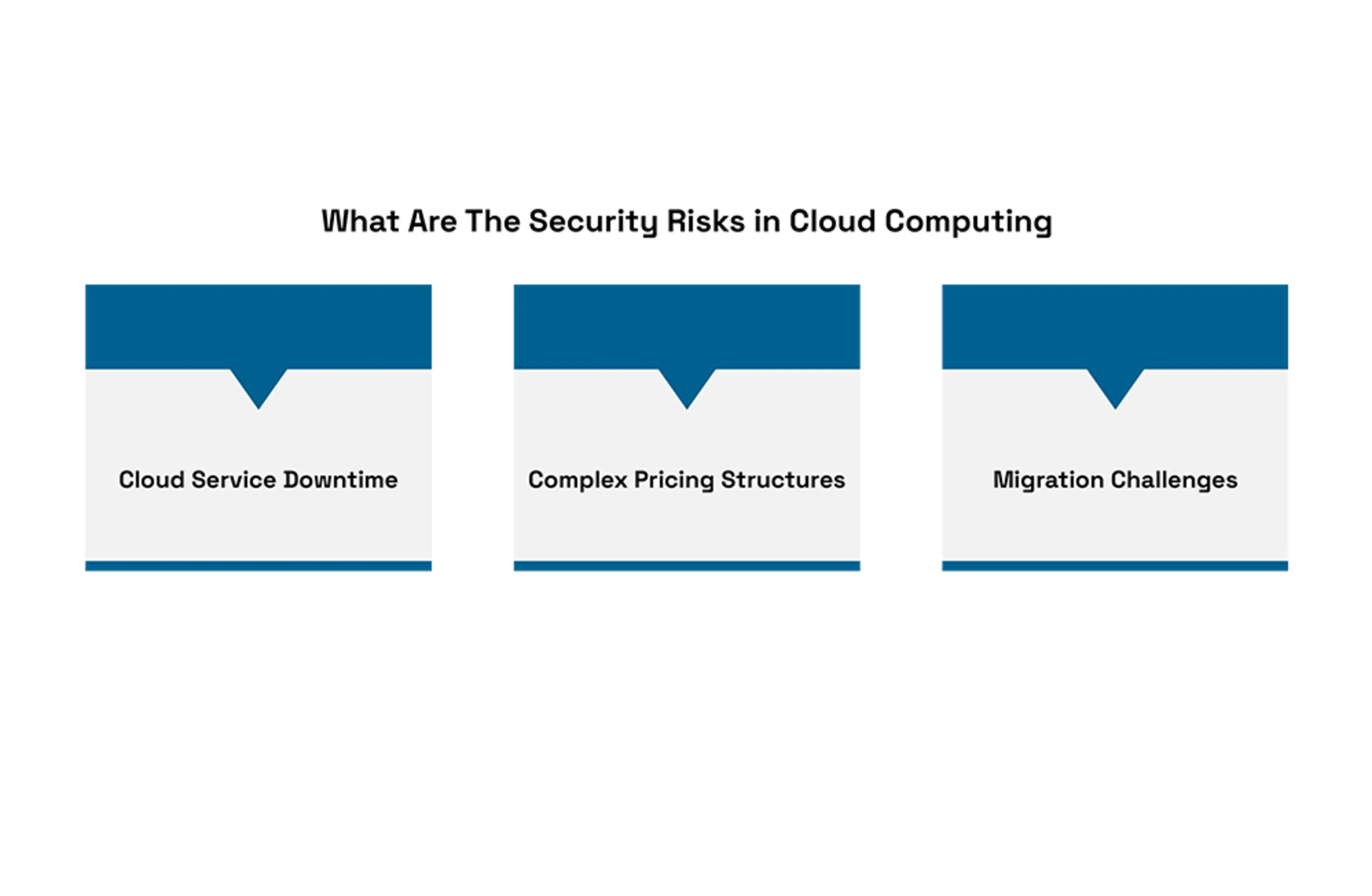
What Are The Security Risks in Cloud Computing?
As of January 2025, the cloud computing scene keeps on developing, presenting new security difficulties and contemplations for associations.
Cloud Service Downtime: While cloud offers make progress toward high accessibility, service lackouts can in any case happen, possibly disturbing business activities. Organizations should ensure robust disaster recovery plans and align SLAs with operational needs.
Complex Pricing Structures: Cloud service pricing models can be intricate, with costs varying based on usage, data transfer, and additional services. This complexity can lead to unexpected expenses if not carefully managed. Organizations should regularly monitor and optimize their cloud usage to control costs effectively.
Migration Challenges: Transitioning to the cloud involves significant planning and resources. Challenges incorporate information move intricacies, application similarity issues, and expected margin time during relocation.
 Expert Insights: The Future of Cloud Computing in Data Centers – Trends, Predictions, and Challenges to Watch
Expert Insights: The Future of Cloud Computing in Data Centers – Trends, Predictions, and Challenges to Watch
The destiny of distributed computing in data centers is molded by patterns like edge registering, quantum figuring, and simulated intelligence mix. These innovations promise faster processing, improved scalability, and enhanced flexibility for businesses. As multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud strategies grow, data centers must tackle challenges such as security risks, downtime, complex pricing, and migration hurdles. The evolution of cloud computing will focus on efficiency, cost reduction, and resilience, providing businesses with more reliable and scalable infrastructure to meet future demands.