In 2025, implementing Zero Trust Security in data centers will turn out to be progressively crucial for battling advancing cyber threats. The model expects no part to be relied on clearly, paying little mind to what its district is inside or outside the affiliation. Key to its prosperity are methodologies like miniature division, which isolates uniqueness. Key to its prosperity are methodologies including micro-segmentation, which isolates different parts of the network to limit lateral movement in case of a breach. Advanced solutions, such as Google BeyondCorp, StrongDM, and JumpCloud, help enforce strict identity and access management controls. Furthermore, organizations, including government bodies like the Department of Defense, are adopting Zero Trust to strengthen security protocols. An organized, staged approach is expected to address likely difficulties and completely incorporate Zero Trust standards across the data center foundation.
What Is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity approach based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the organization, meaning no user, device, or application is trusted by default, regardless of its location. In a Zero Trust model, continuous verification of users, devices, and network traffic is required before granting access to resources. This involves strict identity and access management, micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement within the network, and the principle of least privilege to minimize the exposure of sensitive data. The goal is to reduce the attack surface and prevent unauthorized access, even in the event of a breach.
What Are the Basic Principles of Zero Trust?
The essential standards of Zero Trust rotate around the possibility that trust ought to never be expected, and security should be upheld at each layer of an organization. These standards include:
- Verify Identity Continuously: Before accessing resources, users, devices, and applications must be verified and authorized, with this process occurring at every step of their interaction with the organization.
- Least Privilege Access: Every client, device, and application should simply move toward the specific resources principal for their work. This diminishes the expected effect of a break by restricting admittance to delicate information.
- Microsegmentation: The organization is separated into more modest fragments, and access is completely controlled between these sections. This forestalls horizontal development on the off chance that an assailant accesses one piece of the organization.
- Assume Breach: Zero Trust operates under the assumption that a break could happen suddenly, and thus, security endeavors are planned to distinguish and answer risks quickly.
- Comprehensive Monitoring and Logging: Consistent following of all signal traffic, alongside logging and breaking down movement, is fundamental for distinguishing and relieving threats continuously.

Why Zero Trust Is Important for Modern Data Centers
Zero Trust is the main for modern data centers since customary edge-based security models are as of now not adequate to safeguard against the inexorably complex and successive digital threats. As modern data center frameworks become more interconnected and the labor force embraces remote and half-and-half work models, characterizing and getting the organization’s edge turns out to be progressively difficult. Customary edge-based security approaches are presently not adequate to protect against the developing intricacy and recurrence of cyber threats.
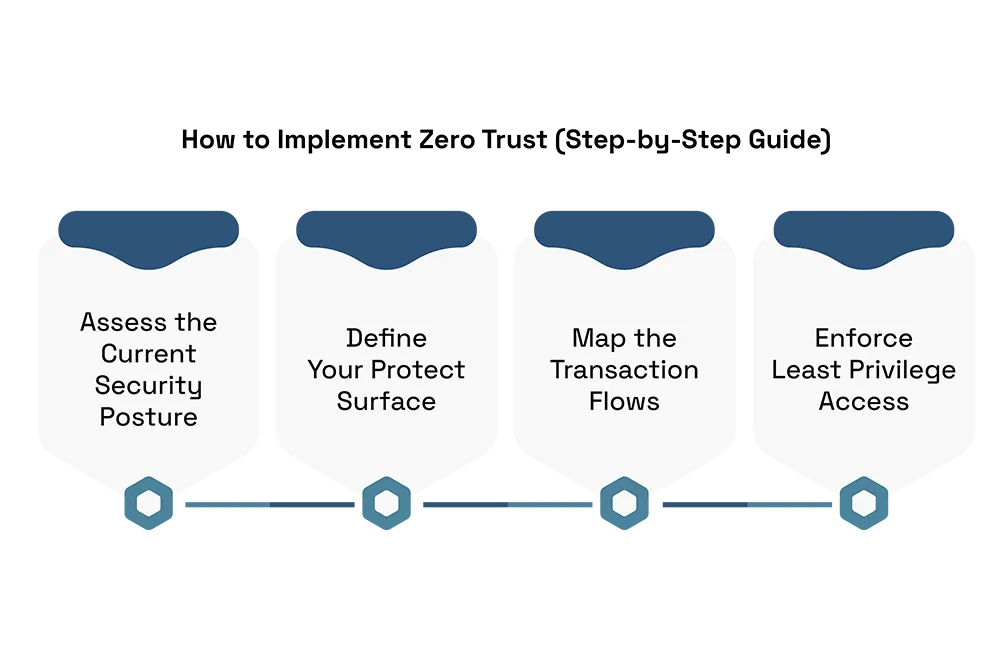
How to Implement Zero Trust (Step-by-Step Guide)
Carrying out Zero Trust includes a vital, staged approach. Here is a step manual for getting everything rolling:
- Assess the Current Security Posture: Survey your current network foundation, security strategies, and instruments to distinguish shortcomings and regions that require improvement for Zero Trust implementation.
- Define Your Protect Surface: Recognize and group your most basic resources, like delicate information, applications, and licensed innovation, to guarantee they get the most elevated level of security.
- Map the Transaction Flows: Understand how data and users interact within the network. This helps in designing access controls and monitoring points for sensitive transactions.
- Implement Strong Identity and Access Management: Send multi-layered affirmation, single sign-on, and work-based permission control to guarantee that just supported clients and devices can get to resources.
- Enforce Least Privilege Access: Grant users and devices the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. Continuously review access rights to prevent unnecessary privileges.
- Segment the Network or micro-segmentation: Separate the network into smaller, isolated segments to lower the amount of the lateral spread of threats and make it harder for attackers to navigate across kinds of areas of the network.
- Deploy Continuous Monitoring and Analytics: Carry out instruments for ongoing observing, logging, and investigating network traffic, client conduct, and access endeavors to distinguish peculiarities and likely dangers.
- Automate and Enforce Security Policies: Utilize computerized frameworks to authorize security arrangements reliably across the organization and immediately answer expected breaks or misconfigurations.
- Test and Validate Security Controls: Regularly test security systems and controls to ensure they are functioning as expected and adapt them based on evolving threats.
- Continuous Improvement and Adaptation: Zero Trust is a constant cycle. Consistently survey and refine your safety efforts to stay aware of arising dangers and changes in your framework.
Common Challenges in Zero Trust Implementation and How to Overcome Them
Common challenges in Zero Trust implementation include:
- Legacy Systems: Overcome by gradually upgrading or replacing outdated systems.
- Complex Deployment: Use automation tools and start with smaller segments for easier implementation.
- User Resistance: Provide training and communication to highlight security benefits.
- Cost and Resources: Justify the investment with long-term security benefits and deploy incrementally.
- Integration: Pick arrangements that flawlessly coordinate with existing devices.
- Continuous Monitoring: Reuse automated and AI-driven monitoring to reduce resource demands.
Picking the Right Answer for Your Zero Trust Implementation
Picking the right answer for Zero Trust implementation involves considering several key factors. In the first place, guarantee the game plan is versatile to oblige your affiliation’s turn of events, including the extension of extra clients, contraptions, and applications. It ought to likewise incorporate consistently with existing security apparatuses, like character the board, firewalls, and endpoint insurance. A far-reaching arrangement is fundamental, covering all parts of Zero Trust, including personality and access to the board, network division, and nonstop observation. Additionally, prioritize user experience by selecting solutions that enhance security without hindering productivity, through features like Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Arrangements that offer robotization and artificial intelligence-driven investigation are likewise essential for constant danger discovery and authorization of strategies. Finally, choose a vendor with a strong reputation and reliable customer support to guide you through deployment and maintenance. By evaluating these factors, organizations can ensure they select the best solution to build a robust Zero Trust security framework.