Software-defined data centers (SDDCS)
The approach improves flexibility, and scalability, and automates and manages better. The SDDC market was valued at USD 85.5 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to increase to USD 311.8 billion in 2030, with the growing need for virtualization, growth of AI and automation, and inception of hyper-converged infrastructure being the major factors. New forms of networking, storage, and orchestration continue to improve efficiency. Additionally, cloud-native apps and automated data centers also create new opportunities. Besides, SDDCs make a thorough method for controlling nearby, private, and public cloud assets and subsequently, improve effectiveness and deftness in tasks.
Enterprises that use artificial intelligence workloads and edge computing along with multi-cloud and hybrid data center security deployment architectures are driving Software-Defined Data Centres (SDDCs) to develop new capabilities. Predictive maintenance performs better through AI-powered analytics and machine learning tools while automated resource allocation and optimized hybrid workload distribution systems emerge because of this integration. SDDCs become more flexible and scalable due to the integration of Kubernetes-based orchestration and containerized applications. American tech giants AWS Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform each invest substantial resources into SDDC development to advance intent-based networks and SDS solutions and stronger security functionalities. The evolution of SDDCs has established them as fundamental elements of today’s digital infrastructure that enables easy cost-efficient and automatically managed data centers.
What is a software-defined data center (SDDC)?
Where all center parts — capacity, register, systems administration, and security — are virtualized and offers as administrations through programming. In an SDDC, control and management of these resources are abstracted from the hardware Component, give someone permission to for more flexibility, scalability, and automation in data center operations.
Using software, SDDCs can dynamically assign resources, make due workloads, and implement security measures. This model reduces reliance on physical hardware, enhances operational efficiency, and enables organizations to scale and adapt quickly to meet changing business requirements.
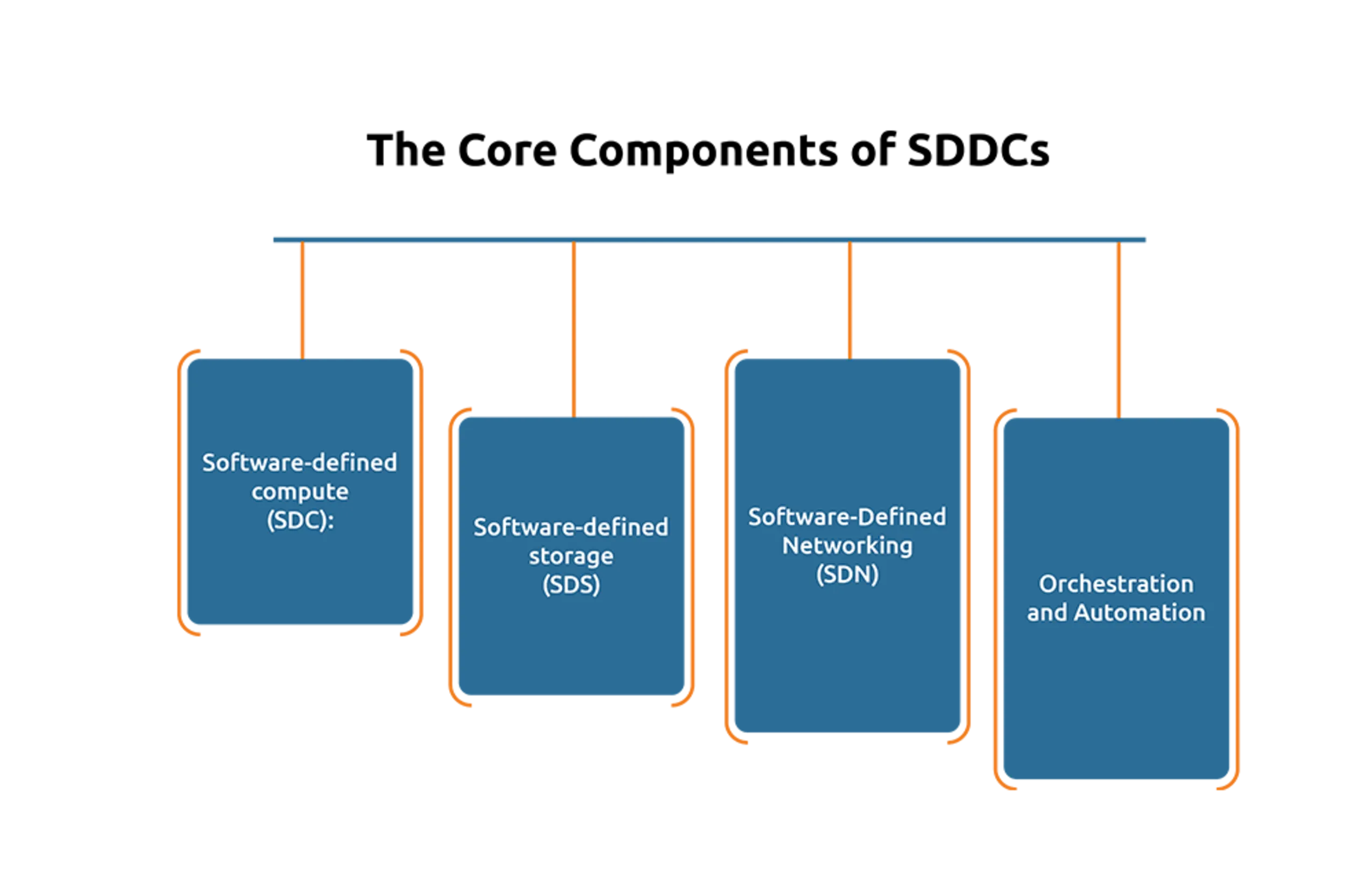
The Core Components of SDDCs
The core components of a Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) include:
- Software-defined compute (SDC): Virtualizes the real servers or compute resources, allowing for efficient resource allocation and management. It abstracts the hardware and enables dynamic provisioning of processing power.
- Software-defined storage (SDS): Virtualizes storage assets, allowing for data to be stored and managed independently of physical storage devices. It offers flexibility in allocating storage space based on demand and increasing scalability.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Virtualizes the network, separating it from the real material infrastructure. SDN allows for centralized control, dynamic configuration, and efficient management of network assets, improving network flexibility and agility.
- Software-Defined Security (SDS): Offers security policies and controls through software, make sure that security mapping are applied consistently across all virtualized environments. This can resemble a firewall, interruption discovery, and robotized security coordination.
- Orchestration and Automation: Facilitates the automation of workflows, deployment, and management assignment. It enables rapid provisioning, scaling, and monitoring of resources across the SDDC, optimizing operational efficiency.
- Management and Analytics: Centralized management platforms that provide a unified interface for monitoring, managing, and optimizing resources. These platforms often include analytics tools that help with performance monitoring, resource utilization, and predictive maintenance.
Together, these components work to create a fully virtualized, flexible, and automated data center environment.
SDDC Architecture
You’re right! The SDDC architecture is structured in layers, each focusing on a specific function to ensure effective and efficient management of resources. Here’s a summary of the key layers you mentioned:
- Physical Layer: This is the foundation of the SDDC, consisting of the actual physical hardware—servers, storage devices, and network devices. It focuses on providing performance, reliability, and stability to support the entire virtualized infrastructure and business operations.
- Virtual Layer: This layer abstracts and virtualizes the physical infrastructure. It provides access to resources such as computing, storage, and networking, and delivers them as services. The virtual layer is responsible for resource allocation, network operation monitoring, and simplifying management, thereby improving overall efficiency and flexibility.
- Management Layer: The management layer standardizes and centralizes the management of the SDDC. It enables orchestration and automation, allowing for easier control and operation of resources through a unified interface. This layer works on the provisioning, scaling, and observing of assets, limiting manual mediation and guaranteeing smoother activities.
Benefits
Software-Defined Data Centers (SDDCs) provide the benefits such as increased flexibility, scalability, and efficiency through virtualized resources. They reduce costs by minimizing hardware reliance, improve security with software-driven policies, and enable faster deployment and simplified management. SDDCs enhance agility, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing demands and innovate more effectively.
Application of SDDCs in Different Industries
SDDCs are applied across various industries to improve scalability, flexibility, and efficiency:
- Healthcare: Secure management of patient data, EHRs, and telemedicine platforms.
- Finance: Agile structure for secure transactions, real-time data analytics, and compliance.
- Retail: Optimized e-commerce platforms, supply chains, and customer experiences.
- Telecommunications: Efficient network management and faster service deployment.
- Education: Supports e-learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and research data management.
- Government: Secure data storage, disaster recovery, and efficient public service management.
Using the Cloud to Accelerate the Move to a Software-Defined Data Center
Utilize the cloud speeds up the progress to a product characterized data center by offering adaptable, versatile, and on-request assets Cloud platforms allow businesses to faster deploy and manage virtualized infrastructure, minimizing the Requirements for large capital investments in physical hardware Component. Cloud services including as infrastructure as a service and platform as a service enable seamless integration with SDDC technologies, easing the transition. In addition, cloud providers offer tools for automation, orchestration, and management, which simplify the setup and operation of SDDCs, increasing the speed of implementation, and reducing operational complexity.
Selecting a Cloud Provider
When selecting a cloud-based SDDC provider, look for:
- Familiar Management Tools: simple to use interfaces to avoid upskilling new software.
- Expertise and Support: Help with a seamless transition to a hybrid environment.
- Flexibility: Support for various SDDC and hardware configurations.
- Managed and Unmanaged Options: Choose between full control or outsourced administration.
- Customization: Capacity to fit the software to meet your one of a kind requirement.
All that you really want to be familiar with Software Defined with Data Centers
virtualize and support all data center assets computing, storage, networking, and security through software instead of hardware. This approach offers a high measure of adaptability, versatility, and mechanization, lessening costs and expanding productivity. Primary parts incorporate Programming Characterized Figures, Stockpiling, Systems administration, and Security, alongside brought-together administration devices. SDDCs coordinate with cloud innovations to speed up arrangements and improve assets of the executives. They are utilized across ventures like medical care, money, and retail to increment spryness and enhance IT tasks.
The Future of SDDCs
The fate of SDDCs is centered around expanded computerization, artificial intelligence-driven administration, and more profound reconciliation with cloud administrations. As organizations request greater spryness and versatility, SDDCs will keep on developing, offering more prominent adaptability in overseeing half-breed and multi-cloud conditions. Advances in edge computing and 5G technology will push SDDCs to support real-time data processing and faster deployments. Additionally, AI and machine learning will enhance resource optimization, security, and predictive maintenance. Overall, SDDCs will play a critical role in enabling smarter, more efficient IT infrastructure for the digital economy.