Introduction
As modern technology advances, the management of heat dissipation has become an essential issue across various industries. From high-performance data centers to consumer electronics, effective cooling ensures maintaining reliability and performance.Liquid cooling technologies have surfaced as a highly efficient alternative, providing superior thermal management. This article explores the principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects of liquid cooling technologies.
Understanding data center liquid cooling
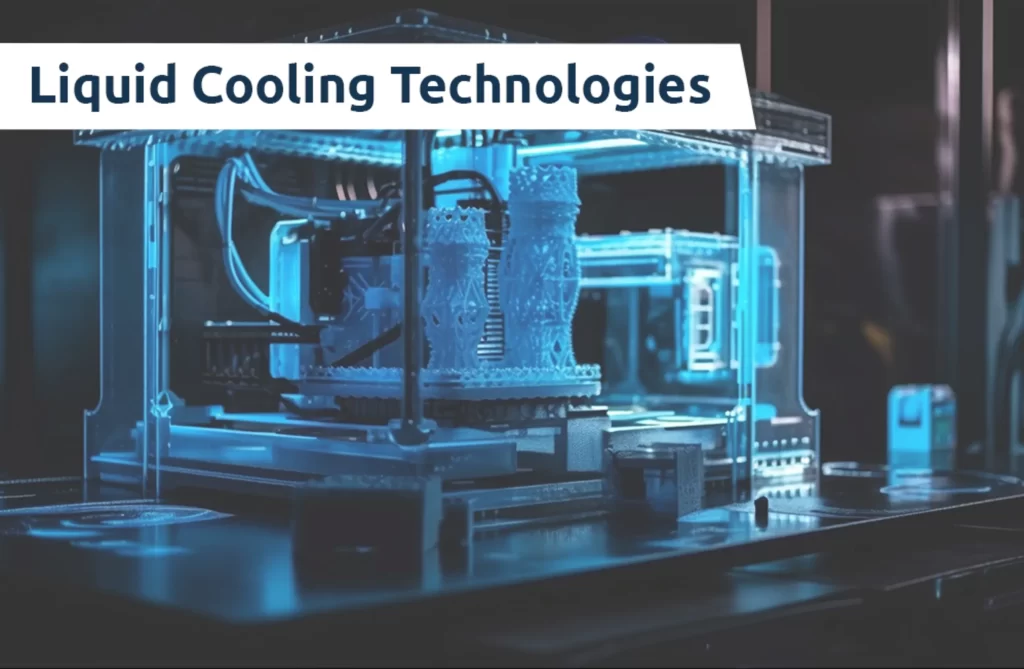
Liquid cooling is a method of heat dissipation where a liquid coolant is used to absorb heat from data center components and transfers it away through circulation, this can carry more heat away efficiently due to their higher heat capacity. This Method utilizes the higher thermal conductivity of liquids compared to air.
In simple words, liquid cooling involves the technology that uses a special water block to conduct heat away from the processor as well as the chipset.
Key Components
A coolant is a liquid, that is typically water or specialized fluids, used to absorb and transport heat within a system.To support this process, a pump circulates the coolant throughout the system,by making sure that efficient heat is transferred. The radiator or heat exchanger then Releases the absorbed heat by the coolant into the surrounding environment. Pipes or tubing Act as channels for the movement of the coolant,by connecting various components. Moreover, cooling blocks act as interfaces that remove heat directly from critical components,Like CPUs and GPUs, improving overall thermal management.
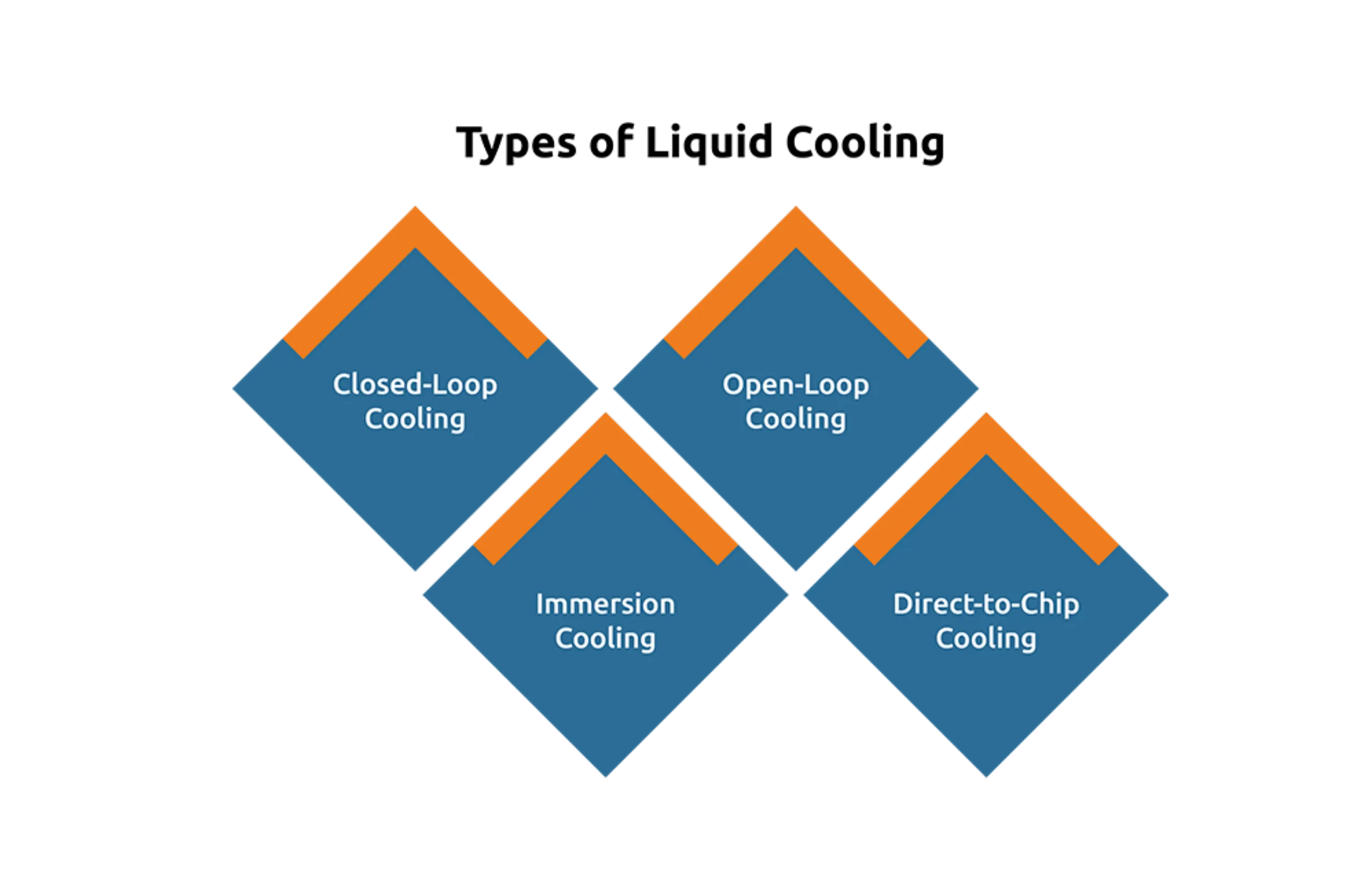
Types of Liquid Cooling:
Direct-to-chip cooling- This involves directing coolant specifically to components, such as processors, to enhance their cooling efficiency.
immersion cooling- This type submerges entire systems in a dielectric fluid for maximizing thermal efficiency.
Liquid Cooling Applications Across Industries
As data centers become more complex, liquid cooling helps in reducing energy consumption and in maintaining optimal server temperatures,as well as in achieving higher rack density. High-performance PCs and gaming systems use liquid cooling to improve performance and minimize noise levels, and for effective heat management smartphones are frequently including liquid cooling.
In industrial applications, robotics, manufacturing systems, and in industrial machinery depend on liquid cooling to ensure stability in high-heat environments. Additionally, electric vehicles (EVs) also depend on liquid cooling for regulating battery temperatures and enhancing motor efficiency, which contributes To increased lifespans and improved safety. Finally, high-performance medical imaging systems, such as MRIs and CT scanners, employ liquid cooling to ensure precision and stability.
Why liquid cooling?
The efficiency of liquid cooling
Liquid cooling stands out for its capability to manage the thermal output of data centers and makes it a key factor while choosing a data center provider. With direct absorbing heat from components, liquid cooling systems can significantly reduce the energy which is required for cooling,and translate into lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Enhancing performance and longevity
Keeping components at optimal temperatures boosts their performance as well as extends their lifespan. Liquid cooling makes sure that even the most heat-intensive operations can run smoothly, supporting the uninterrupted performance of critical applications.
Challenges and Limitations
The initial setup costs for liquid cooling are higher than those for air cooling systems. Additionally, regular maintenance is required to check for leaks, monitor fluid levels, and assess potential corrosion. There is also a risk of component damage, as any coolant leakage can harm sensitive electronics. Furthermore, the disposal of certain coolants must be managed carefully to prevent ecological harm.
Future Prospects
The liquid cooling market is expected to grow fastly, because there is an increasing need for powerful computers & energy efficiency. New technologies, like quantum computing & AI systems, will also need better cooling solutions. Many industries focus on being eco-friendly, liquid cooling is likely to become the standard choice.
Conclusion
Liquid cooling technologies represent a significant advancement in thermal management, addressing the increasing challenges presented by modern systems. While there are Issues to resolve, the benefits in efficiency, performance, and sustainability make liquid cooling an essential solution for the future.
Did you Know?
Data centers liquid cooling market is set for significant growth, with projections indicating growth from $5.1 billion in 2024 to $21.73 billion in 2031.