Cooling System Innovations are used for the development of new technologies to improve the efficiency, sustainability, and performance of cooling systems when focusing on advancements. Like liquid immersion cooling, microchannel liquid cooling, geothermal cooling, smart thermostats, and the use of eco-friendly refrigerants. These innovations are used to reduce energy consumption while maintaining cooling capabilities across many applications like data centers, buildings, and industrial processes.
Key points about Cooling System Innovations:

Modern cooling systems are increasingly focused on efficiency, maximizing heat transfer while minimizing energy usage. To further minimize environmental impact, many innovations prioritize using natural refrigerants and sustainable cooling methods to help lower the overall carbon footprint. Advances in materials also play an important role, with many materials and designs being developed in heat exchangers and many cooling components to improve overall performance. Smart controls are becoming more useful, integrating intelligent systems and sensors to optimize cooling based on real-time conditions ensuring that systems are as easy to use and responsive as possible.
Examples of Cooling System Innovations:
Immersion cooling is added by covering electronic components in a dielectric liquid to directly remove heat, easily managing thermal energy. Another technique, microchannel cooling, utilizes small channels within cooling plates to improve heat transfer to liquid coolants, optimizing cooling efficiency. Geothermal cooling takes advantage of the earth’s stable temperature by using it to provide natural cooling. Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are materials that absorb and release heat during phase transitions, offering thermal storage solutions that help manage temperature changes.
Cooling system innovations include:
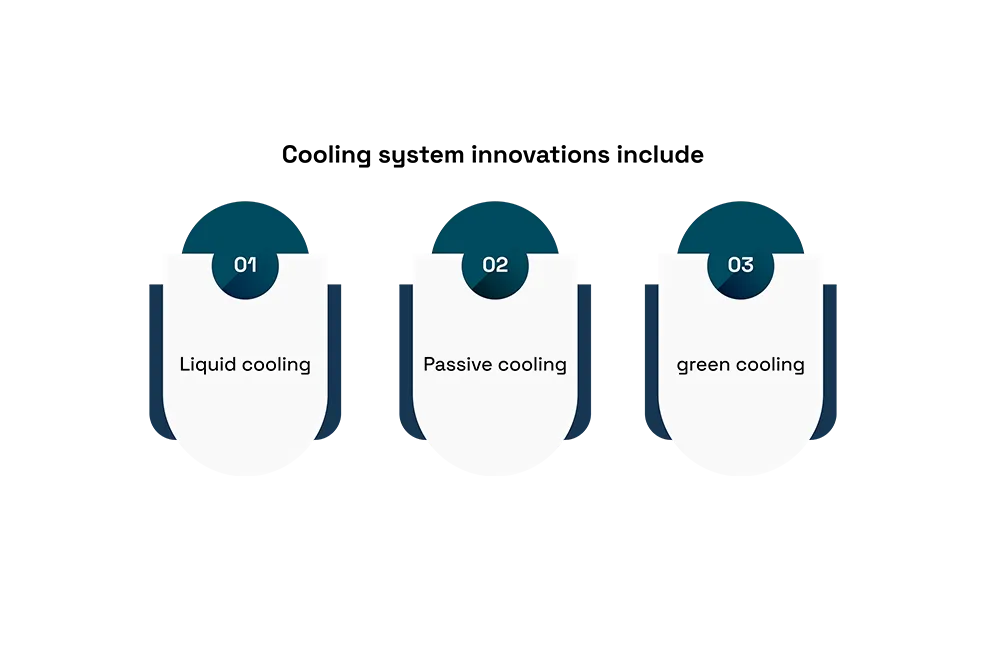
Liquid cooling is a popular technique used to remove heat from equipment by circulating a liquid coolant. One efficient variant of this method is direct-to-chip cooling, which delivers coolant directly to a chip through tubes, helping reduce energy consumption. Another method, evaporative coolers (or swamp coolers), uses water evaporation to cool the air and is particularly effective in dry climates. Air as refrigerant technology compresses a gas, exchanges heat, and then expands it to produce. A low-temperature gas allows for cooling without the use of traditional liquid refrigerants. Passive cooling relies on reflecting thermal energy to the sky and using gravity to collect water. Lastly, green cooling is an innovation developed to make cooling systems more useful and eco-friendly, with a more sustainable approach to temperature regulation.
Liquid immersion cooling
Liquid immersion cooling involves submerging IT equipment in a dielectric fluid that absorbs heat and transfers it to a cooling system. This method can minimize energy consumption, reduce noise, and save space. While also improving the performance and reliability of IT equipment. However, it also requires special hardware, maintenance, safety precautions, and a high initial investment. When developing liquid immersion cooling, you should consider the compatibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of the solution for your data center.
Edge computing
Edge computing is primarily used for the decentralization of data processing and storage from centralized data centers to distributed locations closer to the end users. Edge computing can reduce latency, bandwidth, and data security risks while enabling new applications and services. However, it also introduces new challenges for cooling system design and management, as edge data centers may vary in size, location, and environmental conditions. When developing edge computing, you should consider the availability, reliability, and efficiency of the cooling system for each edge site.
AI and automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation can improve the monitoring, control, and optimization of cooling systems in data centers. AI and automation can analyze real-time data, perform predictive maintenance, detect faults, and dynamically. Adjust cooling parameters such as temperature, humidity, and airflow. These technologies also help improve the energy efficiency, performance, and resilience of cooling systems while minimizing human errors and intervention. When developing AI and automation solutions, you should consider the accuracy, scalability, and security of the solution for your data center.
Conclusion
Cooling system innovations are primarily focused on improving efficiency, sustainability, and performance through a variety of advanced techniques, eco-friendly refrigerants, and smart technologies. These advancements promise to minimize energy use and environmental impact while providing more effective cooling solutions for data centers, database centers, unified computing systems, and other applications.