To protect data center infrastructure in 2025 we need firewalls with an integrated system composed of AI threat analysis and zero-trust access management together with deep packet analysis. The current generation of NGFWS utilizes artificial intelligence to conduct real-time examination of network traffic which detects unusual patterns and possible threats ahead of any damage occurrence. The security standard for data storage in big data is strengthened through micro-segmentation because this technology creates isolated workload areas which stop potential threats from spreading between different sections of the data center infrastructure.
Cloud-native firewalls have gained widespread adoption to secure hybrid along with multi-cloud settings because they enable secure connections between premises-based and cloud-based infrastructure. A vital function of automated firewall policy management tools is their ability to minimize security mistakes while following new security standards. By 2025 successful firewall patterns need to accomplish more than protection against threats because they must use intelligent adaptive defense features to secure data center operations.
What Is Firewall Configuration?
A firewall is an important part of keeping a network safe from data leaks and cyberattacks. To make sure it works actually and needs to be set up correctly by managing domain names and Internet Protocol addresses.
When configuring a firewall, it’s essential to think about the type of network whether it’s public or private. You can create security rules that either block or permit access to help protect against hackers and malware.
Setting up the firewall properly is crucial because the default settings might not offer the best protection against cyber threats.
Importance Of Basic Firewall Configuration
If a firewall is not set up correctly, it can allow attackers to access protected internal networks and resources. Cybercriminals are continuously searching for networks with outdated software or weak security. A report from Gartner predicted that in 2020, 99% of firewall breaks would happen due to misconfigurations.
Most firewalls accompany default settings, and protocols like File Transfer Protocol (FTP) often don’t offer enough protection against cyberattacks. Organizations need to make sure that their firewall settings are tailored to meet the specific needs of their networks.
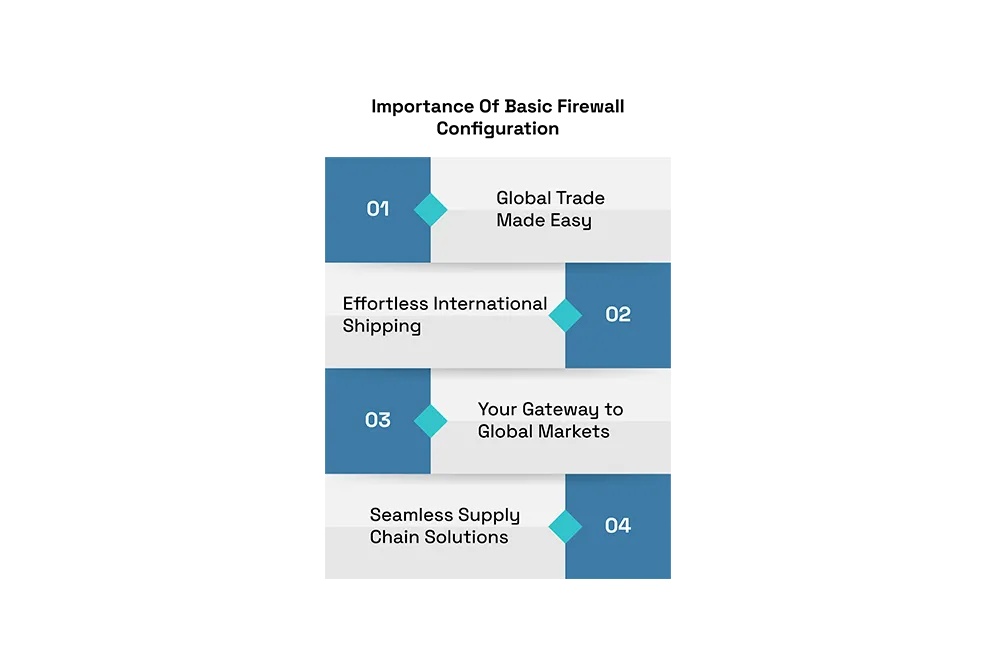
How To Configure A Firewall
Proper configuration is important to support internal networks and stateful packet inspection. Here is how to configure a firewall safely:
- Secure the firewall
Securing a firewall is an essential first step to ensure that only authorized administrators can access it. To do this, it’s important to keep the firewall updated with the latest software. You should never use a firewall in a live environment without properly configuring it first. It’s also crucial to remove or change any default accounts and passwords to enhance security. Each account should have a unique and strong password, and shared user accounts should be avoided. If multiple administrators need to manage the firewall, each should have their account with limited permissions based on their specific roles. Simple Network Management Protocol which assembles information about devices on the network should either be switched off or set up safely. It’s important to control the incoming and outgoing network traffic for specific applications or the Transmission Control Protocol to additionally protect the network.
- Provide firewall zones and an IP address structure
Establishing firewall zones and an IP address structure is crucial for protecting network assets and resources. This involves organizing corporate assets into different zones based on their functions and the level of risk they carry. For example, you might place servers—like email servers, virtual private network (VPN) servers, and web servers—into a special area called a demilitarized zone (DMZ). This zone limits incoming internet traffic to those servers, enhancing security. Generally, the more zones you create, the safer your network will be. However, keep in mind that having more zones also means you’ll need to spend more time managing them. Once you have your network zones set up, it’s important to create a matching IP address structure that assigns these zones to the firewall interfaces and subinterfaces.
- Configure access control lists (ACLs)
Access control lists (ACLs) help organizations control which traffic can enter and exit each zone of their network. Think of ACLs as rules for the firewall that can be applied to each interface and subinterface.
These rules need to be specific, detailing the exact source and destination port numbers and IP addresses. It’s important to include a “deny all” rule at the end of each ACL to block any unapproved traffic. Additionally, each interface and subinterface should have both inbound and outbound ACLs to ensure that only authorized traffic can access each zone. To further enhance security, it’s a good idea to disable public access to firewall administration interfaces and to turn off any unencrypted management protocols.
- Configure other firewall services and logging
Some firewalls can be set up to help with extra services like a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server, an intrusion prevention system, and a Network Time Protocol server. But, it’s important to turn off any extra services that you won’t be using to reduce possible security risks.
Along with this, firewalls should be configured to send logs to a logging service. This is necessary to satisfy the requirements of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard and to secure proper monitoring and compliance.
- Test the firewall configuration
When the configurations are set up, it’s important to test them to ensure the right traffic is being blocked and the firewall is working properly. You can test the configuration using methods like penetration testing and vulnerability scanning. Also, be sure to back up the configuration in a safe place in case anything goes wrong during the testing.
- Manage firewall continually
Managing and monitoring the firewall is essential to ensure it keeps working effectively. This involves checking logs, conducting vulnerability scans, and regularly reviewing the firewall rules. It’s also important to document all processes and continuously manage the configuration to maintain strong protection for the network over time.
Mistakes To Keep Away from While Setting Up A Firewall
While setting up a firewall, it’s essential to keep away from common mistakes that can lead to problems. Here are a few key things to look out for:
Using overly broad policies or incorrect settings can cause issues with servers, like problems with Domain Name System (DNS) and connectivity.
Not paying attention to outgoing traffic can create risks for the network.
Relying only on the firewall for security or using non-standard authentication methods might not fully protect all company resources.
Conclusion
Firewalls are very important to keep networks safe from cyber threats, but they are successful only if they are set up and managed correctly. To ensure strong protection, it’s important to follow best practices like securing the firewall, creating different zones, using access control lists, enabling logging, and regularly testing the system. Ongoing management and monitoring are also crucial to deal with changing security challenges. By avoiding common mistakes and adjusting firewall settings to fit the organization’s needs, businesses can greatly reduce vulnerabilities and improve their overall cybersecurity.