Introduction
Cooling systems are important for confirming the smooth activity of data centers. They help by making sure that IT devices stay inside the right temperature and humidity levels indicated by the manufacturers. In the case of cooling isn’t successful and the data center server can be overheated that can cause devices to fail which leads to downtime and increased costs.
Today, there are new challenges like Increased rack densities, more energy use, and the need to be more environmentally friendly. Due to this finding effective and reliable cooling solutions is a higher priority than at any time.
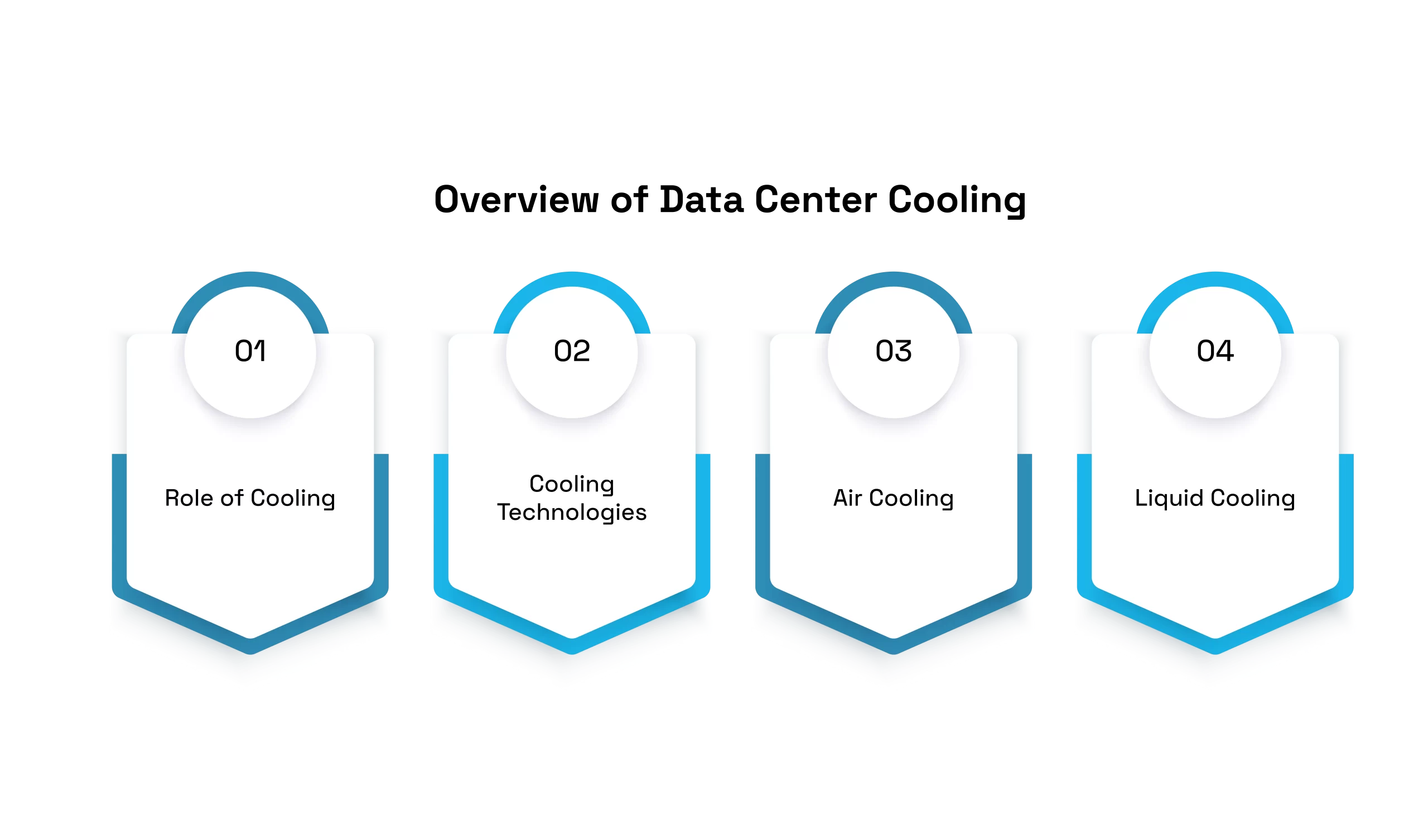
Overview of Data Center Cooling
Role of Cooling:
Cooling systems keep temperatures at the right levels to stop hardware from breaking down and to ensure everything runs smoothly.
Cooling Technologies:
Air Cooling: This is a method of cooling that uses air conditioners and fans to keep items cool.
Liquid Cooling:
This is a technique for heat bust where a liquid-cooled server is adapted to absorb heat from data center components and transfer it away through flow.
Hybrid Cooling:
This method combines both air and liquid cooling systems to be more efficient.
Key Metrics:
PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness): This measures how energy-efficient a cooling system is. The most ideal PUE is 1.0 which implies all the energy is utilized really.
Cooling Load Factor (CLF):
This helps evaluate how well the cooling system’s capacity matches the actual amount of heat produced by the IT equipment.
Best Practices for Data Center Cooling
Conduct a Thorough Assessment
Analyze Airflow: Use computer modeling to study how air moves in the data center.
Regular Inspections: Check cooling systems often for wear and inefficiencies.
Find Hotspots: Use thermal imaging to spot areas that are too hot.
Optimize Airflow Management
Hot Aisle/Cold Aisle Setup: Authorized server racks in a way that keeps hot and cold air flowing separately for better cooling.
Seal Gaps: Close any openings and holes to stop air from getting away.
Use Blanking Panels: Put panels in empty spaces in the racks to keep hot air from mixing with the cool air.
Leverage Advanced Cooling Technologies
Liquid Cooling: Great for dealing with high-quantity Operations like AI and machine learning.
Immersion Cooling: Overflows servers in a special liquid that conducts heat away.
Evaporative Cooling: This uses the procedure of vaporization to cool down, which saves energy compared to regular air conditioning.
Uses Monitoring and Automation
IoT Sensors: For monitoring the temperature, humidity, and airflow in real-time Use smart sensors.
AI Cooling Systems: Implement systems that consequently change cooling based on how much work is being finished.
DCIM Tools: Use data center management tools for predicting maintenance needs and optimizing cooling.
Embrace Energy-Efficient Designs
Variable Speed Fans: Use fans that change their speed based on how much cooling is needed.
Energy-Efficient AC Units: Choose air conditioning units that save energy and have features like economizers.
Modular Designs: Build flexible systems that can adapt and reduce energy waste.
Leverage Geographic and Environmental Factors
Col Locations: Build data centers in cooler climates or places that naturally help with cooling.
Free Cooling: Take advantage of outside air or water to reduce the need for mechanical cooling.
Underground or Underwater Data Centers: Consider these options for naturally stable temperatures.
Benefits of Implementing Cooling Best Practices
Advanced cooling systems boost reliability by reducing equipment malfunctions and downtime. They also promote energy savings as more efficient cooling methods consume less power. This enhancement in energy efficiency aligns with sustainability goals by aiding in carbon footprint reduction. Furthermore, these systems are cost-effective, cutting cooling costs and potentially increasing the lifespan of equipment. In summary, improved cooling solutions offer numerous advantages for both operational performance and environmental impact.
Case Studies
Google Data Centers: Google employs artificial intelligence to improve the efficiency of cooling resulting in a 40% decrease in cooling energy costs.
Microsoft’s Project Natick: Microsoft has created underwater data centers that take the benefits of natural cooling to improve the efficiency of energy.
Equinix’s Free Cooling: Equinix uses airside economization in areas with suitable climates to lessen the dependence on traditional cooling units.
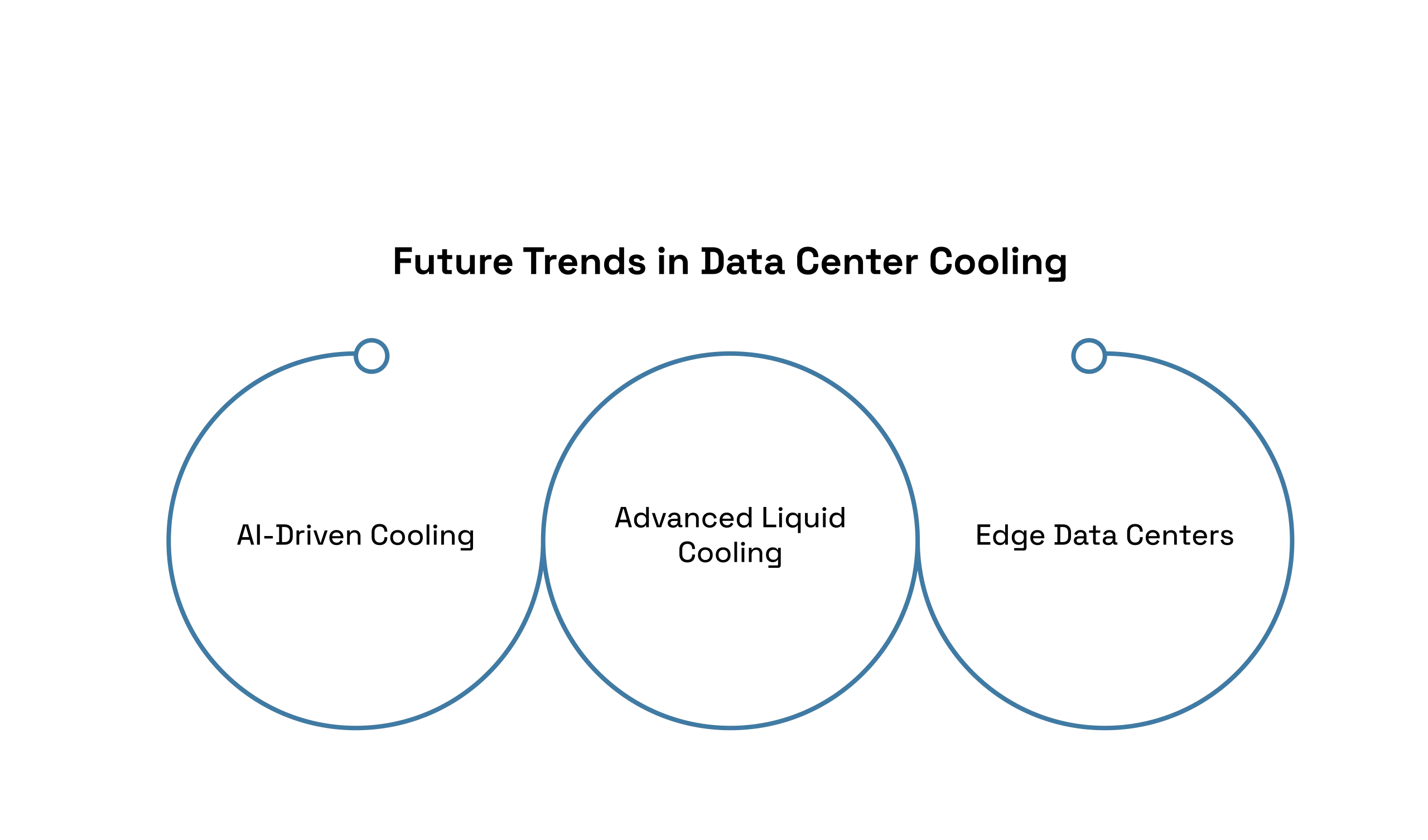
Future Trends in Data Center Cooling
AI-Driven Cooling: This technology uses real-time data and predictions to reduce cooling systems.
Advanced Liquid Cooling: More facilities are starting to use immersion cooling, which is effective for high-performance computing.
Edge Data Centers: These smaller local data centers need compact and efficient cooling solutions.
Sustainable Practices: There is a growing focus on using cooling systems powered by renewable energy.
Hydrogen and Helium Cooling: These are new and upcoming options for future cooling technologies.
Conclusion
Efficient cooling is important for making data centers continuous, reliable, and low-cost. By following the best practices mentioned, companies can make sure their data centers are ready for the future, use energy carefully, and are good for the environment.