What Is Data Center Automation?
Data center automation involves leveraging technology to handle and execute tasks within a data center without the need for manual intervention. This includes activities such as configuring servers, managing workloads, and overseeing system performance. The aim is to improve the efficiency of data center operations by automating repetitive and error-prone tasks.
Data center automation is part of a larger area called IT process automation (ITPA), which focuses on reducing manual work across all IT activities. This can involve automating the creation of virtual machines or coordinating complex tasks that involve different systems and applications.
To effectively automate a data center, it’s important to sort out which tasks can be automated and then utilize the right devices to do so. Additionally, it’s essential to continue improving and changing these automation processes as the requirements of the data center change.
Why is data center automation important?
Data center automation is important because businesses today deal with a huge amount of data and need to operate quickly. Relying on people to monitor, fix problems, and manage tasks can be too slow and risky. Automation helps make many operations run almost on their own. Ideally, data center providers can use APIs to connect with public clouds, allowing customers to easily move their data or workloads between different cloud services.
Most data center automation is done through software that gives centralized access to various resources in the data center. This access allows for the automation of tasks related to storage, servers, networks, and other data center management tasks.
Data center automation is Highly valuable because it frees up human computational time and Delivers insight into server nodes and setups Automates routine techniques like patching, updating, and reporting Produces and programs all data center scheduling and monitoring tasks Implements data center processes and controls in agreement with standards and policies.
Data center automation is a crucial component of modern IT environments, aiming to enhance efficiency, reduce manual tasks, and improve operational performance. By utilizing tools like APIs, configuration management systems (such as Ansible, Puppet, and Chef), and platforms like OpenStack, organizations can automate repetitive tasks like server management, patching, and reporting. This automation not only streamlines operations but also frees up valuable human resources for more strategic tasks. However, implementing automation can present challenges, such as resistance to change, integration issues with legacy systems, and security concerns. Despite these hurdles, data center automation is becoming indispensable for businesses looking to scale operations, improve efficiency, and maintain competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
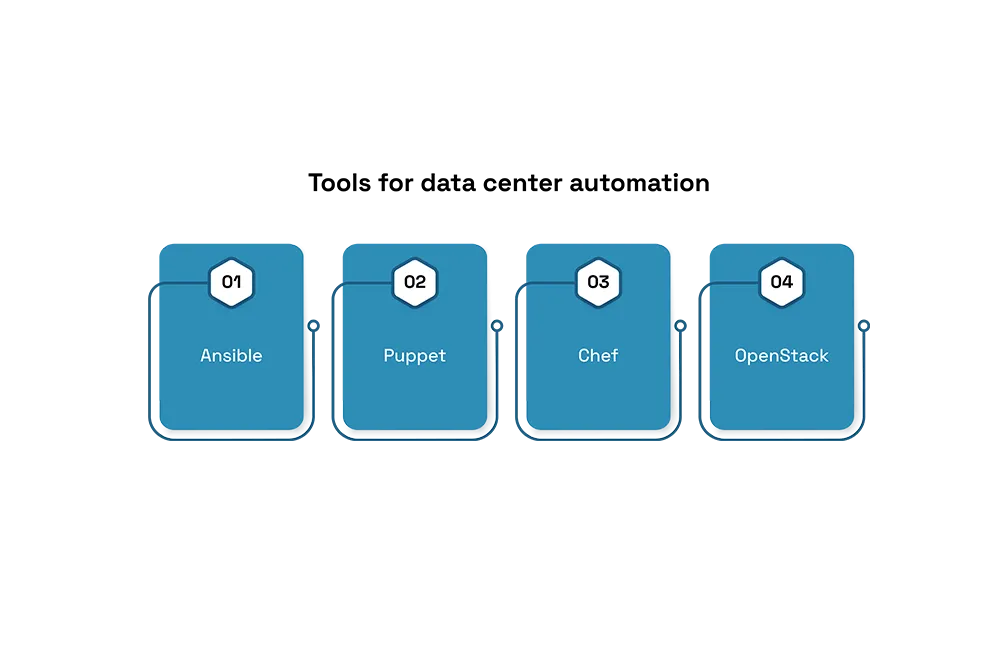
Tools for data center automation
APIs
An API is a set of Guidelines that helps different software applications to communicate with each other. When infrastructure provides APIs for tools like configuration management and OpenStack. It can help companies to save time, money, and resources. It also helps ensure that developers have a consistent environment to work in.
Configuration management tools
Ansible – Ansible Tower is a tool from Red Hat that helps to automate tasks for Red Hat Linux and other systems. It provides a framework that supports various practices like agile development, DevOps, and continuous delivery. It makes it simpler for groups to cooperate and deal with their software projects efficiently.
Puppet – Puppet is a tool that helps IT professionals automate tasks like installing software. It uses a special language to create instructions and workflows that the Puppet system follows. This means that Puppet provides a common way to manage different devices and systems. IT departments use Puppet to simplify and automate complex processes that involve many types of hardware and software.
Chef – Chef is a set of tools that can be used for free or purchased commercially. It’s built using the Ruby programming language and allows users to create “recipes” that automate tasks. These recipes can manage everything from an entire system to just one part of it. It has three main parts: Chef, Inspec, and Habitat. You can utilize these parts all alone or together to make a complete system for managing DevOps processes.
OpenStack – OpenStack is a system that helps manage large groups of computing power, storage, and networking resources in a data center. You can control these resources using a dashboard or through the OpenStack API. Essentially, OpenStack acts like an operating system for building cloud infrastructure or managing local resources as if they were part of a cloud. This means it automates tasks like creating, removing, and managing virtual servers and other virtual resources. Additionally, Red Hat offers a version of OpenStack that is open-source and designed for businesses, providing better support.

Implementation Strategy
Step 1: Check Your Current Setup
Make a list of all your hardware, software, and workflows. Look for areas that are not working well or causing problems.
Step 2: Set Goals
Decide what you want to achieve. For instance, you might want to reduce downtime by 20% or speed up the setup of new frameworks by half.
Step 3: Choose the Right Tools
User-friendly pick tools, work smoothly with one another and can grow with your requirements.
Step 4: Plan How to Integrate
Create a step-by-step plan to add automation tools without interrupting your current operations.
Step 5: Train Your Team
Hold workshops and provide hands-on training to assist your team learn how to utilize the new tools.
Step 6: Test It Out
Run a trial of the automation in a controlled setting to see how well it works.
Step 7: Roll It Out Fully
Gradually implement the automation across the entire data center.
Step 8: Keep Improving
Regularly check and change the automated processes to make them more proficient.
Various Challenges in Implementing Automation
Implementing automation can come with a few difficulties. One major issue is protection from change, as employees might worry that automation could lead to job losses. There can also be coordination issues, particularly when older systems don’t work well with new tools. Also, the initial costs for some automation tools and training programs can be quite high, which may be a challenge for certain organizations. In the end, there are security risks to consider. Automated systems can become focuses for cyberattacks if they aren’t properly protected.
Conclusion
Data center automation is at this point not optional. It’s essential for modern IT environments. By using the right tools and techniques organizations can improve proficiency, scalability, and cost savings.







